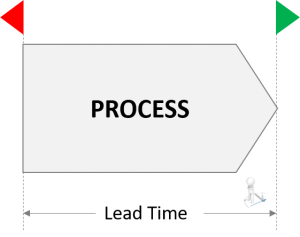
The Lead Time
The Lead Time, is the time that elapses between the beginning and the end of a process..
Lead Time is measured on the production processes, but also administrative processes.
For example, it could be:
- The time taken for the realization of a product on an assembly line.
- The processing time for the recording of a customer order.
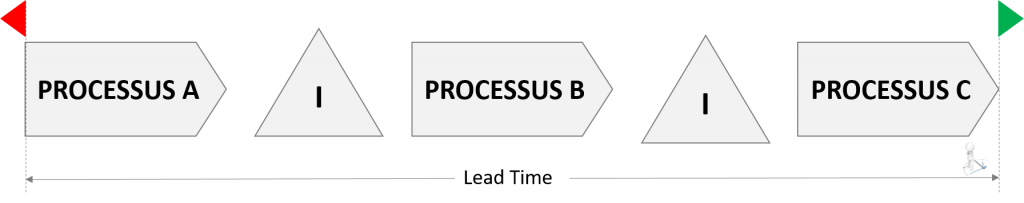
In general, the Lead Time identified in the business concern the crossing time of a set of processes. This can range from raw material procurement to the shipping department via sawing, machining, assembling, packaging.
- Often the entire process combines production processes and administrative processes.
- Between processes, there can be storage areas. The crossing time is also measured here. This measurement is done by applying Little’s Law.
How is defined Lean Time
Lead Time is set to a product or a business process. For example, for the manufacture of a finished product, it will leave the supply of the main component, until arrival at the shipping department of the finished product.
Lean time can be estimated or measured :
Estimated:
- Process: compared to the routing time
- Inventory: Use of Little’s law (LT = Inventory quantity / Average consumption)
Measured:
- Timing
- Followed a piece from start to exit
It is better to have a Lead Time measured. This is generally done when making a VSM. This allows to increase in parallel the sources of waste and avoid maximum database errors.

Interest of Lead Time
Lead Time is a key performance indicator of Lean : speed determines the performance of the organization.
More the crossing time is short :
- The faster you put products or services available to the customer (Time-To-Market). This is a major strategic factor that can give among other the opportunity to take a competitive advantage.
- The faster the costs incurred are covered (Time-To-Cash). This is a very important point for the cash of the company.
Other concepts related to Lead Time
Cumulative Lead Time :
It is the addition of different Lead Time :
- Purchasing Lead Time
- Production Lead Time
- Distribution Lead Time
Door To Door :
This is the crossing time from arrival at the front door of the plant, until the exit.
Apparent depth of process:
This is the Lead Time seen by the customer (which is different from the global Lead Time, if for example, the customer is delivered from a warehouse of finished products)